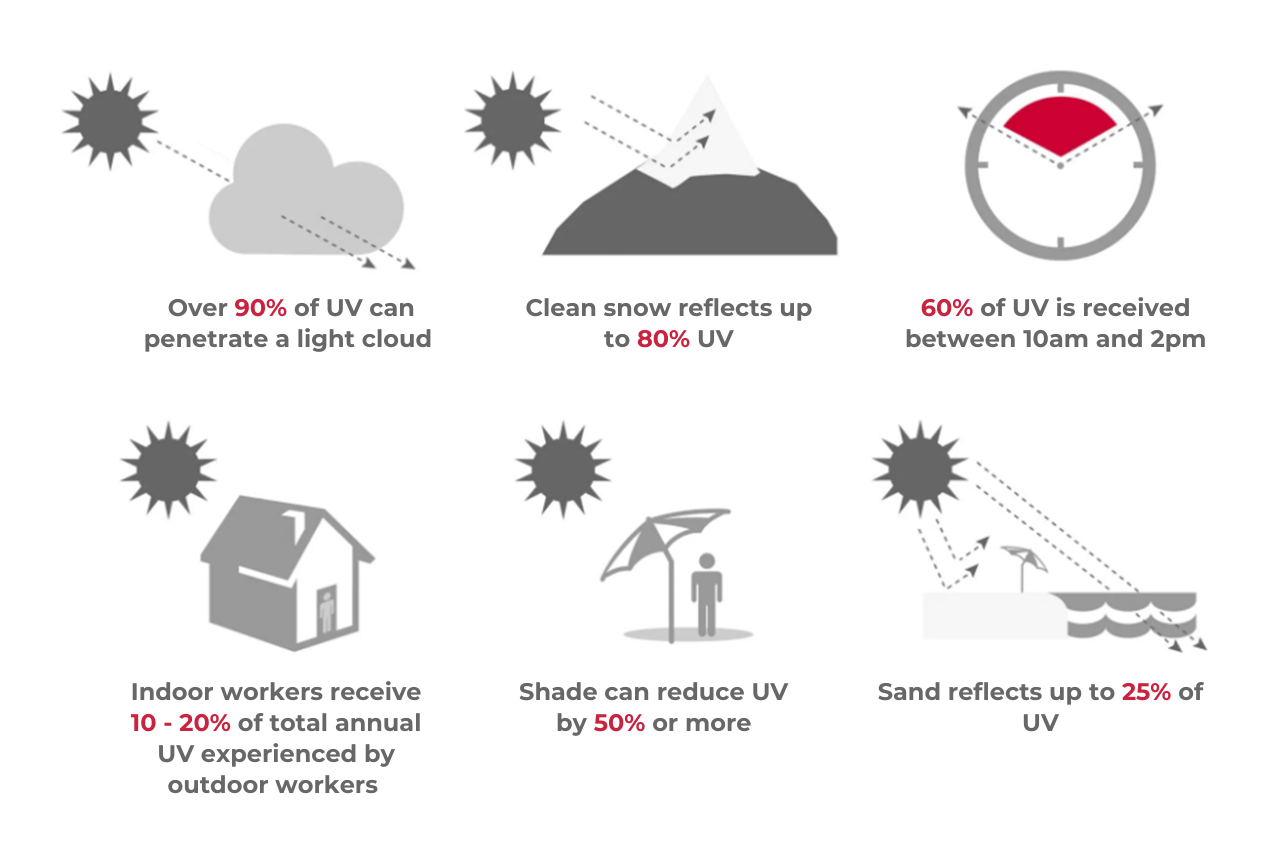
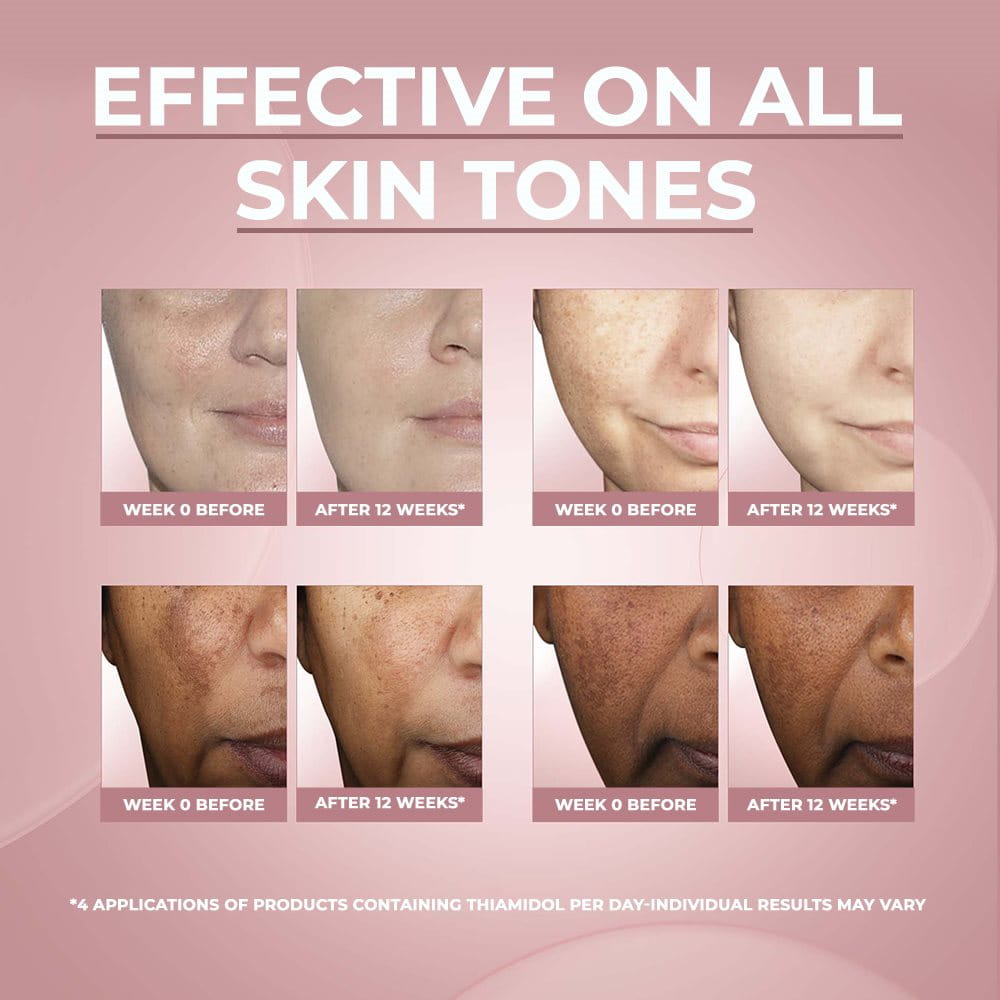
Among the many skin concerns plaguing people across the world, hyperpigmentation and melasma are among the most recurring on the list.
Often people mistake one for the other, but they are diverse skin conditions with distinct symptoms, causes, and treatments.
Understanding the difference between melasma and hyperpigmentation is important to curate the right skincare plan.
Keynotes:
- Hyperpigmentation is a common term referring to all kinds of skin discolorations.
- Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation mainly caused by hormonal changes in your body.
- The appearance and causes of melasma is what differentiates it from other types of hyperpigmentation.